728x90
- 자료구조
- 연결 리스트
- 이진 트리
- 스택
- 큐
- 해시
- 정렬
- 버블 정렬
- 선택 정렬
- 삽입 정렬
- 퀵 정렬
- 힙 정렬
- 알고리즘
- 재귀 함수
- 너비 우선탐색(BFS)
- 깊이 우선탐색(DFS)
- 다익스트라
퀵 정렬(Quick Sort)
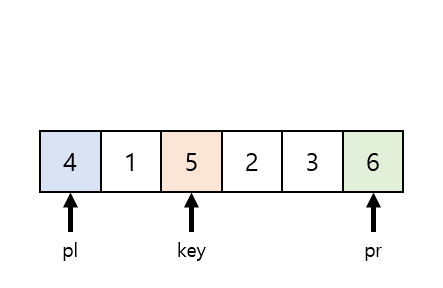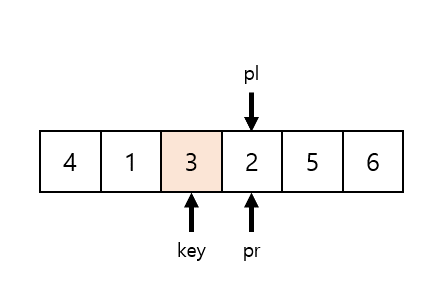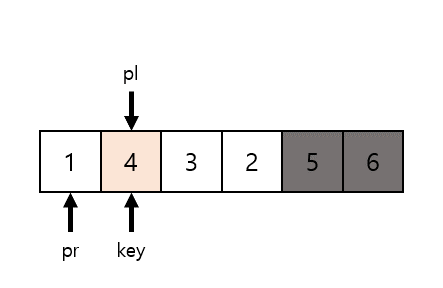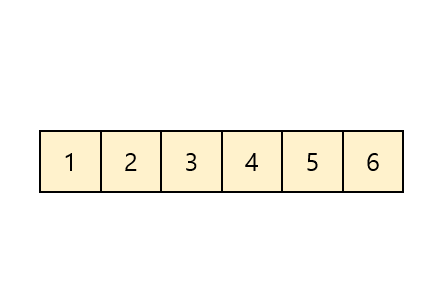
퀵정렬은 이름 그대로 아주 빠른 속도를 자랑한다.
중앙값(Key)을 기준으로 왼쪽에는 작은값 오른쪽에는 큰값을 넣어주고
2파트로 나눠서 반복한다.
이처럼 큰 문제를 작은 문제로 나눠서 해결하고 이를 합치는 방법을 분할 정복이라고 한다.
퀵 정렬은 분할 정복을 이용한 정렬이다.
시간 복잡도 : O(n * log(n))
소스코드
#define __main
#ifdef __main
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10
void Init(int arr[]) {
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++) {
// 임의의 정수 입력
arr[i] = rand() % 10000;
}
}
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int tmp;
tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void Quick_Sort(int arr[], int left, int right) {
int pl = left;
int pr = right;
int key = arr[(pl + pr) / 2];
do {
while (arr[pl] < key) pl++;
while (arr[pr] > key) pr--;
if (pl <= pr) {
swap(&arr[pl], &arr[pr]);
pl++;
pr--;
}
} while (pl <= pr);
if (left < pr) Quick_Sort(arr, left, pr);
if (pl < right) Quick_Sort(arr, pl, right);
}
void Print(int arr[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++) {
printf("[%d] -> %d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
printf("\n--------------------\n\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[MAX_SIZE];
Init(arr);
Print(arr);
Quick_Sort(arr, 0, MAX_SIZE - 1);
Print(arr);
return 0;
}
#endif'프로그래밍 > C언어' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 재귀 함수 (0) | 2020.11.19 |
|---|---|
| [정렬] 힙 정렬 (0) | 2020.11.17 |
| [정렬] 삽입 정렬 (0) | 2020.11.09 |
| [정렬] 선택 정렬 (0) | 2020.11.06 |
| [정렬] 버블 정렬 (0) | 2020.11.04 |



